SAP (GRC) Access Control User Access Review (UAR)
SAP User Access Review is a centralized, automated process that provides a workflow-based review and approval mechanism to validate that users have only the necessary permissions required for their job roles, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Managers and role owners perform periodic reviews of user access against scheduled requests generated by the system based on the organization’s internal control policy.
Key Features for SAP Access Control UAR
- Automated scheduling. Scheduled reviews are triggered automatically at defined intervals, i.e., quarterly, biannually, or annually, eliminating manual efforts to track when reviews are due and who needs to be reviewed.
- Dynamic user selection. The system can automatically identify users whose access needs to be reviewed based on pre-defined criteria.
- Delegated review process. Instead of the central IT team, the review process is delegated to managers or role owners who can assess the actual job function of targeted users or accounts, making the process more accurate and efficient.
- Workflow-driven review management. The workflow-based UAR process automatically generates requests and sends them to the designated reviewers for approval or rejection. If needed, escalation or re-routing paths are defined to expedite the process, providing a transparent and auditable trail. Workflow processes can be configured in a way that, if reviewers mark a role or permission as unnecessary, an automatic process can be triggered to remove that access.
- Comprehensive reporting and audit trail. SAP Access Control provides dashboards and extensive reporting functionalities to monitor the progress and outcomes of User Access Reviews. All actions taken during the review process are logged, including approvals, rejections, and role removals to create an audit trail and comprehensive report for regulatory compliance.
- Multi-system integration. SAP Access Controlis primarily focused on SAP systems; however, it can extend its UAR capabilities to other integrated systems with connectors, providing a holistic view for user access governance across the organization’s diverse systems.
- Business role reviews. Using SAP Access Control, reviews can be conducted not only on technical roles but also on business roles, simplifying the review process that can limit access to a complete business function rather than reviewing multiple technical roles or permissions.
Key Benefits of SAP User Access Review Process
The User Access Review process with SAP Access Control can standardize and automate the entire review lifecycle. To reduce the amount of manual labor with spreadsheets and ad-hoc communication, the UAR process is driven by workflows, automated notifications, and consistently applied system rules enforcing internal controls. Dashboards with progress status and detailed reporting improve the operational efficiency and effectiveness of the UAR process.
- Business managers take ownership of their team’s access based on the context of business operations.
- Internal control or audit teams benefit from standardized processes with audit trails to effectively monitor compliance and identify potential risks.
- IT teams are less burdened with the manual access provisioning and de-provisioning challenge, focusing on compliance and technical implementations.
Participants in the SAP User Access Review Process
- Administrators are typically IT or Security team members responsible for the overall setup, configuration, and maintenance of the UAR process. They are responsible for administrative tasks such as canceling open review requests, regenerating new review requests for users who were canceled in the previous cycle, and an optional admin review before the UAR workflow launch.
- User managers are key participants in the UAR process. They are the direct managers of end users and are best suited for primary review, as they possess the most in-depth knowledge of end-user job functions and required access.
- Reviewers are individuals who perform assessments during the UAR cycle. They can be the direct manager of end users or the role owners of specific end users’ business roles. Reviewers are responsible for evaluating each access granted to an end user based on their job functions and roles needed. They can approve of retaining a role, remove it if it’s no longer necessary, or forward the request to another approver if required.
- Role owners are individuals or teams responsible for business roles within an organization. In the UAR, these role owners serve as specialized reviewers, focusing on the roles they own. They review and validate the access granted to end users who fall under the roles they own and provide insight into the purpose and implications of the access granted by their roles.
- Coordinators are users who facilitate and monitor the progress of the UAR process, resolve any process issues, i.e., assigning a relevant reviewer to a request with no valid reviewer, and generally ensure that the review process stays on schedule. They send reminders to reviewers with pending tasks, assist reviewers with any questions regarding the process or technical details, escalate delayed reviews to management, and control the efficient completion of the UAR process on time.
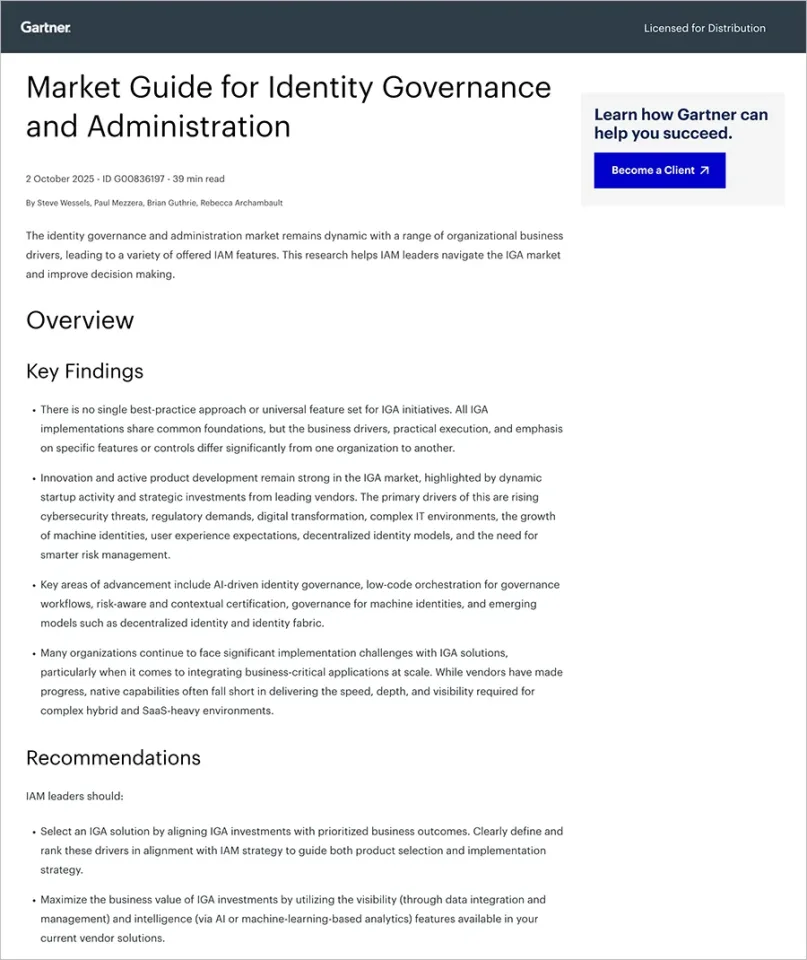
User Access Review Process Flow
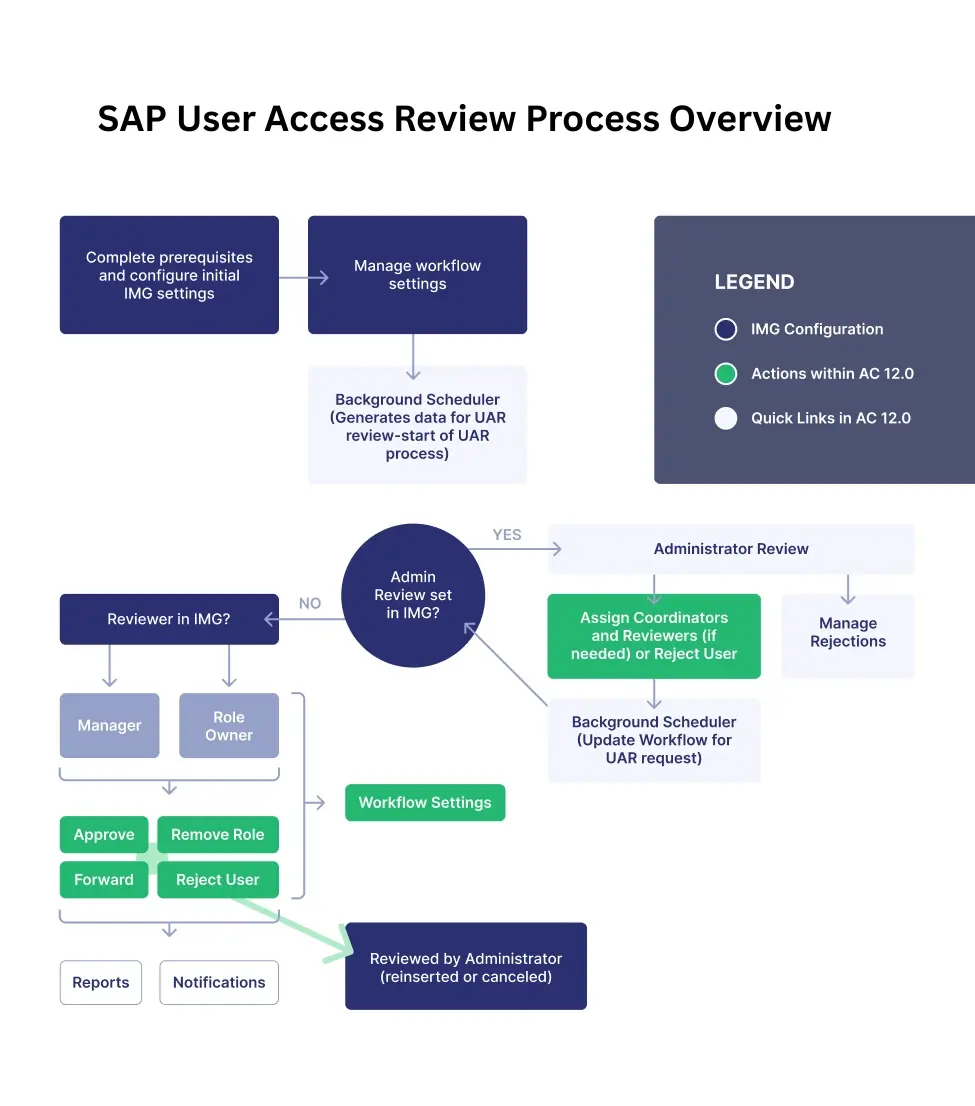
Source: SAP
Roles in User Access Reviews
Roles are a set of access privileges and permissions assigned to a user that determine the business activities a user can perform and which parts of the user interface can be accessible or visible. In SAP ERP, users can be assigned different types of roles to access the system according to the permissions assigned to that role.
Role Types in UAR
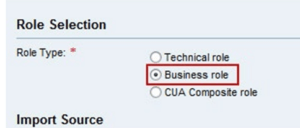
- Technical Role: Authorization privileges assigned to a single user in one or more systems. These are the granular levels of permissions associated with specific transactions, reports, and data access. Changes to user job responsibilities will require careful evaluation in the UAR process to remove or add technical (single) roles.
- Business Role: A logical grouping for technical and business roles, representing the job functions or responsibilities within an organization. These roles are mapped to technical roles, which translate the business-level needs into the required system-level authorization.
- CUA Composite role: Grouping multiple single roles, assigning multiple single roles’ authorization privileges to the end user. In the UAR, composite roles assigned to a user would be evaluated based on the current job functions. This evaluation determines whether the user only requires a subset of single roles within the composite role, indicating over-provisioning, or if all the single roles of the composite role are needed.
Typically, business roles are assigned to end users, which contain technical roles comprising single, composite, or derived roles that have the actual authorization for specific systems.
Choosing Role Types in the UAR Process
Choosing the role types in the UAR process depends on the level of detail and the efficiency required in the review process. Technical roles provide detailed pictures of actual user access, allowing reviewers to see precisely what transactions, objects, and organizational levels a user can access.
However, if you have many technical roles, the review process will be lengthy and complex. Reviewers might struggle to understand role assignments without a business function or job role. Including business roles alongside technical roles, reviewers gain the necessary business context for the access being reviewed. This enables business managers, who may not be familiar with SAP technical roles, to review and certify access to clearly defined business functions efficiently and effectively.
The decision to include technical roles only or include business roles as well impacts the report level generated for the UAR process. When business roles are selected for review, the report displays only the assigned business roles, and the system allows drilling down to view the underlying technical roles.
How to Generate a User Access Review Job in SAP Access Control
To generate a UAR job:
- Log in to SAP Access Control and select Access Management.
- Select Background Scheduler.
- Click Create.
- From the Schedule Activity dropdown, select “Generates Data for Access Request UAR Review” and check the option “Generate UAR for Business Roles”.
Process Options in SAP Access Control
SAP Access Control offers multiple process options to tailor the approval workflow according to the organization’s specific needs, based on compliance, business, and security requirements.
Admin Review
The admin review option provides designated administrators with the opportunity to validate request data before it is sent to the primary reviewers. Typically, GRC or security teams validate the accuracy and completeness of data generated for the UAR request, i.e., correct users, roles, and systems are included in the review. Administrators can edit the requests to rectify any missing or incorrect data. For example, if a user’s department has changed and the UAR job is still assigned to their old manager, administrators can correct this information before the actual workflow triggers. They can remove duplicate or entirely incorrect requests, preventing unnecessary workload for reviewers.
Reviewer Stage
This is the primary decision-making stage in the UAR workflow, where a thorough review is conducted. The system allows us to specify whether the reviewer will be the direct manager of the end user whose access is being reviewed, or that responsibility can be assigned to the role owner(s) of the specific role(s) being reviewed. Managers are best positioned to review the roles as they understand the day-to-day responsibilities of their direct reports and can make informed decisions for the user’s current access. The rationale for designating a role owner as a reviewer is that role owners are responsible for the purpose and consequences of a role, so they can best determine whether a user should have access to the specific role.
Security Stage
The security stage is mandatory if automatic provisioning is disabled and the security team manually implements approved access changes, such as removing roles from a user assignment that the reviewer rejected.
Even if automatic de-provisioning is enabled, it’s better to include a security stage for final validation to avoid potential conflicts in proposed changes. When the security stage review is included in the approval workflow, security personnel must be able to modify or override primary approvers’ decisions, as they are responsible for implementing the approved changes, whether manually or by monitoring automated provisioning.
Additional Approver Stage
Organizations can add an extra layer of approvers, allowing custom approval steps in the UAR workflow, derived from the Custom Approver Determinator rule that determines the additional approver, based on specified criteria. Common fields used for criteria in UAR CAD are:
- Application: Specific SAP application or system for which access is being reviewed.
- Request type: Request types if they are being differentiated, e.g., user provisioning, role assignments, sensitive data.
- Role: specific roles defined in UAR requests.
Workflow Configuration
After deciding the stages to include in the UAR workflow, it’s crucial to configure communication and escalation channels to ensure timely and effective review completion. Inform users and stakeholders about UAR tasks, status, or changes with proper email notifications, set reminders to complete reviews in a defined period, and define escalation paths to a higher authority in case of conflict with a suggestion.
Configuring Email Notification
The content of the notification should clearly state the purpose and required actions within the context of UAR, including the users or roles under review, links to relevant UAR requests, deadlines, and contact information for any queries.
Specify recipients as primary approvers, additional approvers, the security or compliance team, and the administrator for respective stages of review.
Notification of access revocation for information purposes to the end user or their manager if access was revoked during UAR, explaining the decision. The subject of the notification should be informative, concise, and easily understandable. The body should provide detailed instructions, relevant links, and contact information for support.
Setting Reminders
Decide how often reminder emails are sent, i.e., every 3 days or weekly, until the review is completed. The reminder notification should indicate it’s a reminder, containing required actions details, due dates, and links to pending UAR requests.
Specifying Escalation
Define a time threshold on each workflow stage. If UAR requests remain in a stage after the defined time threshold, the system automatically triggers an escalation, which should be reflected in the audit trail of the request. Specify in the configuration that upon escalation, the system should revoke the access of the approver who did not review the UAR request by a specific date defined in the deadline. Often, a grace period is also established, and reminders notify users about this period, providing information that access will be removed after the specified time.
Performing Automatic Provisioning
Automatic de-provisioning enables SAP Access Control to remove marked roles at the end of the UAR request workflow. When a reviewer marks a role for removal from a user, the provisioning engine processes the removal without requiring further approval steps, thereby reducing administrative workloads and improving compliance by implementing prompt enforcement of access changes. If automatic provisioning is not enabled, a security stage must be added in the workflow to allow the security team to modify the access according to the review.
Prerequisites
Synchronization Job
The repository object sync job ensures that data in SAP Access Control is up-to-date and consistent with the connected SAP systems, including user master data, role data, and HR master data.
Steps to configure the synchronization job are as follows:
- Log on to the SAP Access Control system.
- From the SAP Easy Access screen, select Tools → Customizing → IMG → Execute Project.
- Select SAP Reference IMG → Governance, Risk and Compliance → Access control → Synchronization Jobs → Repository Object Sync.
Importing Roles
The Importing Roles functionality enables administrators to import existing roles from connected SAP systems into the SAP Access Control repository.
Steps to import Roles are as follows:
- Log on to the frontend SAP Access Control system.
- Navigate to Access Management → Role Mass Maintenance → Role Import option.
- Define Role Import criteria. Specify the criteria to filter the roles you want to import. Criteria may include:
- Role Type
- Import Source
- Description
- Created By
- Created On
- DateLast
- Changed By
- Role Lock Status.
- Select Role Data. Provide the role attribute, such as:
- Name
- Description
- Role Type
- Specify role authorization data such as:
- Associated Authorization Objects
- Field Values.
- Select the Preview option to review the selected roles and ensure the criteria are correct. Confirm the number of roles and their relevant information. The system may flag that the selected roles already exist in the GRC database, and importing could result in overwriting existing information.
- Schedule the job to run in the background immediately or at a specified time. Click Submit to initiate the import process.
IMG Configurations for User Access Reviews
Managing IMG Configurations for UAR
SAP Implementation Guide (IMG) configuration allows administrators to configure settings related to UAR and generate Data for UAR requests.
- Log in to the backend system of SAP Access Control (AC). From the SAP Easy Access screen, navigate to Tools → Customizing → IMG → Execute project.
- Click on the SAP Reference IMG button. Navigate to Governance, Risk and Compliance → Access control → Maintain Configuration Settings.
In the AC Configuration Settings Overview, define the standard fields in the context of UAR.
- Param Group: It’s a logical grouping of related parameters to organize and categorize configuration settings. For UAR, this often includes “UAR Review” or “UAR workflow”.
- Parameter ID: A unique identifier for a specific configuration parameter, a system uses this ID to recognize and apply the parameter’s values. These values can be in a sequence for each Param Group, i.e., 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007.
- Priority: Defines the precedence of the parameter value.
- Description: A short explanation of the purpose and function of the Param Group, i.e., “Admin review required before sending task to reviewers.”
These parameters and their values can define a configuration behavior, for example:
| Param Group | Param ID | Parameter Value | Priority | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UAR Review | 3000 | Yes | 0 | Admin review required before sending the task to the reviewer |
| Access Request Business Role | 3108 | No | 0 | Do not copy manual role assignment changes during repository sync |
If the user does not have a manager or the role does not have an owner, selecting ‘No’ in parameter 3000 will result in no workflow being generated for the request. Additionally, reviewers, such as managers or role owners, must have a coordinator; otherwise, the request will not be sent to a reviewer.
There are additional customizations that define the operational characteristics of UAR requests, such as request types, priority, and rejection reasons, to distinguish UAR requests from other access control requests. Priority levels, such as low, medium, and high, define the urgency of the request, and rejection reasons provide a standardized list of reasons, e.g., “Role not relevant” and “User left department”.
Defining an Email Reminder
- Log on to the backend SAP Access Control system. From the SAP Easy Access panel, navigate to Tools → Customizing → IMG → Execute Project → SAP Reference IMG.
- Navigate to Governance, Risk and Compliance → Access Control → Workflow for Access Control → Maintain Text for Custom Notification Messages.
- On the documentation Maintenance Screen, define the body of the notification message using General Text as Document class.
- Navigate to Governance, Risk and Compliance → Access Control → Workflow for Access Control → Maintain Custom Notification message.
On the Notification Messages Overview screen, specify:
- Sender
- Subject,
- Attachments if applicable.
- Navigate to Governance, Risk and Compliance → Access Control → Workflow for the Access Control → Maintain MSMP workflows.
At the MSMP workflow configuration screen, select the relevant ProcessID and choose the step Variable & Templates, create a notification template, and map the template to the message class.
- Choose Step 7 “Generate Versions” and save to activate the configuration.
- Navigate to Governance, Risk and Compliance → Access Control → Workflow for Access Control → Maintain Background for E-mail Remainder
At the Define Background Job screen, specify the background job information for the remainder of the messages.
Specifying the Service Level Agreement
Service level agreements (SLAs) for UAR can be defined in terms of measurable metrics, such as the period for approving, denying, or fulfilling UAR requests, the frequency of role certifications, and the timeframe for addressing access conflicts or deviations.
- Log on to the backend SAP Access Control system. From the SAP Easy Access panel, navigate to Tools → Customizing → IMG → Execute Project and select SAP Reference IMG.
- Navigate to Governance, Risk and Compliance → Access Control → Use Provisioning → Maintain Service Level Agreement
At the Service Line Agreement Overview screen, create a new Service Level Agreement using SAP_GRAC_USER_ACCESS_REVIEW as the process ID.
Managing Coordinators
The coordinator-to-reviewer mapping can be modified in the SAP Access Control system.
- Log on to the front end of the SAP Access Control system. Navigate to Access Management → Compliance Certification Reviews → Manage Coordinators.
- On the Manage Coordinator screen, select a mapping and modify the settings such as:
- CoordinatorID
- ReviewerID
- Respective names or emails.
- The administrator can delete a coordinator-to-reviewer mapping by selecting the mapping and clicking ‘Delete’, then pressing ‘Yes’ on the confirmation message box.
Managing the UAR Workflow
The User Access Review workflow is primarily managed through a Multi-Staged Multi-Path (MSMP) workflow configuration. This powerful and flexible framework enables highly customizable workflow definitions and automates the process of generating and approving UAR requests.
- Log on to the backend SAP Access Control system, from the SAP Easy Access screen, choose Tools → Customizing → IMG → Execute Project and select the Reference IMG button.
- Navigate to Governance, Risk and Compliance → Access Control → Workflow for Access Control → Maintain MSMP Workflows
- Configure the global escalation settings and escape conditions by selecting the SAP_GRAC_USER_ACCESS_REVIEW processID. Select the Change Mode for Display/Change option to configure settings as required.
Global Escalation settings define what happens to a workflow item, i.e., a UAR request, if it is not acted upon within a specific time frame. A notification can be sent to an escalation agent, i.e., the manager’s manager or a security administrator. The request can also be rerouted to an alternative reviewer.
Global Escape Conditions are criteria under which a workflow bypasses certain stages or even gets terminated, i.e., approver not found, and ensures that requests don’t remain stuck at these stages.
After setting global escalation settings and escape conditions, the next step is to Maintain Rules. These rules determine the workflow logic, such as who should approve, the path the request should take, and the conditions that must be met for specific actions.
Function Module: These are ABAP-based logic to determine complex organizational rules or to calculate risk score, typically used for logic that cannot be easily achieved with the Business Rule Framework plus (BRFplus) rules.
- BRFplus is used by non-technical users to define rules using a graphical interface, determining approvers based on user attributes, such as department equal to “Sales” or role equal to “Sales Representative”.
- ABAP Class is a custom ABAP code encapsulated in a class, used for defining rules if logic is complex.
- BRFplus Flat Rules are simple rules that express statements as simple as “if-then” or lookup tables.
These rules can be utilized in the process of ID for initiators, routing, agents, or notification variables.
v. Next step is Maintain Agents. Here, you can define an agent for workflow stages for either notification or approval.
- Directly Mapped Users: Users assigned directly with the User ID as an agent.
- PFCG Roles: An agent is selected based on a specific SAP security role, and any user assigned to that role can act as an approver.
- PFCG User Groups: An agent is selected according to the SAP user group.
- SAP API Rules: These rules are determined by the associated Function module or BRF+ rules logic. Specifically, the Manager of the user or any user available in the managerial hierarchy is identified in the HR database.
vi. Next step is Variables & Templates to maintain notification templates and variables that are sent at various stages of the workflow.
- Template ID: is a unique Identifier for the notification template, which the system will trigger for a particular notification type.
- Message Class: is a standard SAP ABAP Dictionary object that groups related messages. It helps identify which pool of messages the system should use when sending a notification.
- Message Number: is the specific number within the defined message class that corresponds to the actual text of the notification message.
- Docu. Object: links the notification template to a documentation object that provides additional details. It is helpful for administrators and users to understand the purpose of the content being sent in the message.
vii. Next step is Maintain Paths, add or modify values for Path ID and Path Description fields.
A Path defines a sequence of stages that a workflow request will follow. The Path ID is the unique identifier, e.g., UAR_PATH_DEFAULT_PATH, and the Path Description explains its purpose.
Specify the following fields when configuring the stages:
- Stage Seq Number: Defines the order of the stages.
- Stage Config ID: Identifier for the stage configuration.
- Stage: Description: Details of what the stage’s purpose is.
- Agent ID: Who is responsible at this stage?
- Approval Type: types of approvers, i.e., single or multiple.
- Routing Enabled: Indicates whether the workflow can be rerouted from this stage based on specific conditions.
- Escalation Type: Indicates how escalation is handled at this particular stage, e.g., notify, auto-approve, auto-reject, re-route, no escalation.
- Escalation Time Mins: Determines how long a request should be idle before the escalation process begins.
- Escalation Agent: The Agent ID (User, Role, or Rule) who receives the escalation request or notification.
Viii. Within the configuration of each stage, define the specific actions that an agent can perform on the UAR request.
RT Config Change OK: Enables the approver to modify specific routing configurations within the request.
Email Group enables the approver to send an email to a predefined group of users.
- Reroute: Allows standard users to reroute the request to a previous stage. For the administrator, the reroute option is available to reroute the request to any other reviewer.
- Display Review screen enables the approver to view the detailed UAR review screen, where they can see the user’s access, roles, and make decisions.
- Reject User: Allows the approver to reject the access for specific users within the UAR request.
- Change Request Det: Allows the approver to modify specific details of the workflow request.
- Comments Mandatory: Requires approvers to enter comments when approving or rejecting a request.
- Forward Allowed: Allows the approver to forward the request to another individual for action.
- Approval Type: Allows approvers to approve requests for all the roles in a request or only those that belong to them.
- Reaffirm Approve: Requires the approver to confirm their identities before approving requests.
- Next step is to configure Main Route Mapping to determine which path a workflow request will take based on specific conditions.
- Rule ID: Add the ID of the rule (function module, BRFplus, or ABAP class) that will be evaluated to determine the path of the workflow.
- Rule Result Value: The result value returned by the rule, i.e., if the BRFplus rule outputs “CRITICAL_PATH”, then the workflow will follow the path mapped to “CRITICAL_PATH”.
- Path ID: Unique ID of the workflow path to follow for the result.
- The last step is to Generate Versions, which generates a new version of the workflow.
MSMP workflows are version-controlled; changes made to the workflow will not take effect in previously generated requests. They will appear only in requests generated with the new version of that workflow.
Generating Data for User Access Reviews
Generating Data for UAR in SAP Access Control is Critical for the UAR Process. A scheduled job is configured to retrieve the user-to-role relationship and role usage data.
- Log on to the frontend SAP Access Control system, navigate to Access Management → Scheduling → Background Scheduler
- Select Create, and the Schedule details will appear.
- At the Schedule Details page, provide the schedule name, i.e., UAR Job, and select Generate Data for Request UAR review from the dropdown menu on the schedule activity field.
- Choose the Recurring plan field and select yes, with recurring date and time range, along with the frequency and recurrence interval.
- Choose Generate UAR for Business Roles if you want to include business roles as well.
- The next step is Variant, where specific parameters and filters are defined for UAR Data generation.
- On the Next page, review all the changes, and select Finish.
- After configuring the scheduled job, the system displays the status of each job with status:
- Planning: The Job has been defined and saved, but has not yet been executed or is scheduled to start later.
- Completed: The job has finished its execution successfully.
- Terminated: The job has been manually stopped or cancelled by the administrator.
- Error: The job encountered a critical error during its execution.
Performing User Access Review in SAP Access Control
After the UAR requests are generated, the system automatically generates work items for each reviewer. These work items appear in the Work Inbox app of reviewers or are sent to reviewers via email.
The Work Inbox app displays all pending requests with high-level information for each item, including Request ID, Request Type, Subject, and allows for a drill-down to view detailed information about the request. Reviewers can take actions as follows:
- Approve: confirms that the user’s access is still valid and required for job functions, and subsequently, the Role is not removed.
- Remove Role: The Reviewer determines that all or a specific role is no longer required or excessive and subsequently triggers the remediation process for removing the role(s) from the user.
- Forward: The reviewer forwards the request to another reviewer for a reason, such as the original reviewer is out of the office or the request was incorrectly assigned.
- Approve and remove options: Reviewers can approve or reject specific roles. Each role has an option to select, such as approve, remove, or no action.
Manage Rejections
Authorized users can search for rejected users, view search results, sort them according to criteria, and generate new review requests as well. Authorized users can also cancel review requests generated for those requests that have not been completed.
- Log on to the frontend of the SAP Access Control system, navigate to Access Management → Compliance Certification Reviews → Manage Rejections.
- On the Manage Rejections screen, specify search criteria and click on the search button. Rejected users will appear in the Result table.
- To select users for UAR request generation, select the respective user’s rejected requests and choose the Generate Request button.
This process marks the user for inclusion in a new UAR request when the UAR Review Process Rejected background job is executed. - To cancel request generation, select the respective rejections and choose the Cancel Generation button. This process is used when a rejected request will not be resubmitted or is no longer relevant, and administrators can mark the rejected requests as “Closed” or “Cancelled”.
- To generate new Request for Rejected Users, navigate to:
Access Management → Scheduling -? Background Scheduler.
Select the create button, and the Schedule Details step appears.
- Add Schedule Name field, i.e., UAR Job. In the Schedule Activity field, select Generate New Request for UAR rejected request from the drop-down list. Add the Recurring plan and choose whether the job recurs. If so, define recurring dates and time ranges, along with frequency and recurrence intervals.
- In the Start Immediately field, choose whether to start the job immediately, and in the Start Time field, specify the date and time for the job to start. Click the Next button, select Variant, and click Finish.
User Access Review History Report
The UAR Review History report provides a comprehensive history of UAR requests, detailing the actions taken during access review, including approvals, rejections, and comments. The History Report will display details such as Campaign Name or ID, campaign status, start and end dates, scope (including users, roles, and systems), and reviewers. For each user, details of the data, including access reviewed, reviewer’s decision, justification, date of review, and status of remediation, will be included.
Conclusion
In today’s ever-changing IT landscape, organizations are turning to cloud solutions more than ever to simplify access governance while keeping compliance and security a top priority. User Access Review (UAR) in SAP Access Control offers a comprehensive framework designed to reduce the risk of unauthorized access by facilitating regular, organized, and fully auditable reviews of user permissions.
With its user-friendly workflows, adaptable configuration options, and seamless integration with a range of SAP products, businesses can more effectively analyze and access data, identify discrepancies, and take prompt corrective actions as needed. Additionally, its multi-language support enables global teams to easily engage with the system, thereby enhancing accessibility and efficiency across diverse organizational settings.