Separation of Duties (SoD) is a fundamental principle in risk management, ensuring that key tasks are divided among multiple users to reduce the risk of fraud, errors, or malicious activities. By preventing any one person from having unchecked control over critical functions, businesses can safeguard themselves against potential financial or operational damage. This concept is especially crucial in areas such as accounting and information security, where the potential for harm—whether intentional or inadvertent—is high.
As a result, many organizations today—especially those in finance—enforce strict separation of duties across various departments, including finance, IT, and security, to ensure regulatory compliance and protect against significant risks. However, achieving and maintaining effective SoD remains a continuous challenge for businesses.
What is Separation of Duties (SoD)?
SoD is an internal risk management control for preventing fraud and error in financial transactions. SoD ensures that there are at least two users who are responsible for completing a critical task that has financial consequences or can impact financial reporting.
SoD processes break down tasks, which can be completed by one user, into multiple tasks. The goal is to ensure that control is never in the hands of one user, either by splitting the transaction into 2 or more pieces, or requiring sign-off approval from another party before completion.
Payroll management, for example, often faces error and fraud risks. A common SoD for payroll is to ask one employee to be responsible for setting up the payroll run and asking another employee to be responsible for signing checks. This way, there is no short circuit where someone could pay themselves or a colleague more or less than they are entitled to.
Breaking tasks down prevents risks, however, it does come with other costs. For one, it can negatively impact business efficiency. Additionally, stricter SoD enforcement can lead to an increase in costs and complexity and require organizations to add more staff. This is why many organizations apply SoD only to the most vulnerable and mission-critical components of their environment.
Understanding the benefits and ROI of new technologies is critical as organizations move towards automating internal processes like the monitoring of SoD risks.
Download The Forrester Total Economic Impact™ of Pathlock.
Why is SoD Important?
Separation of duties plays a key role in implementing and maintaining security and compliance. It impacts multiple departments and having a robust SoD framework offers many benefits.
SoD is Critical to Maintain Regulatory Compliance
One of the key regulations that underscores the importance of SoD is the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (SOX). Passed in the wake of major corporate accounting scandals, SOX requires companies to maintain strong internal controls for financial reporting, with SoD playing a critical role. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) mandates that companies establish clear internal controls, and enforcing SoD is an essential part of compliance.
SoD Can Reduce Human Error
When SoD is correctly implemented, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of human error in critical financial activities. When every critical transaction is performed by multiple users, there is a much higher chance one of those users will notice an error and correct it.
It is important to realize that risks in financial reporting do not only stem from malicious users—they can also result from careless users or honest mistakes, which can dramatically skew financial reporting.
SoD Can Increase Efficiency
It is often thought that SoD creates inefficiency, because it requires adding more roles that were not originally needed. However, if SoD is carefully planned, it can lead to specialization which can actually promote efficiency. If you separate financial departments into well-thought-out roles, each of which is carried out by a highly trained, specialized user, each user will do their work faster and more accurately.
Here are a few ways to improve organizational efficiency in an organization implementing SoD:
- Understand what each employee does best and what type of work they prefer doing. It is often possible to make several employees happier and more productive by trading non-conflicting duties between them.
- Identify duplication among roles and ensure that each task or duty is only carried out by one employee.
- Analyze permissions across similar employees, to make sure that employees who should have similar jobs on paper have similar entitlements in the IT systems where they work.
- Ensure each member of the team clearly understands their duties and has the appropriate skills to perform them.
- Create written job descriptions to make it clear to everyone on the team what are each member’s responsibilities.
Why Do Companies Struggle with SoD Implementation?
Companies often struggle with implementing separation of duties (SoD) due to several reasons. One major reason is the conflict between security and efficiency. On the one hand, SoD is critical to preventing fraud and misuse of control in a process. On the other hand, breaking tasks down into separate components can negatively impact business efficiency. Companies are often hesitant to sacrifice efficiency as it can affect their bottom line, resulting in weaker control and increased risk of fraud.
Additionally, implementing SoD can also lead to increased costs, process complexity, and staffing requirements, which can be daunting for organizations, particularly smaller ones. This may lead to companies only implementing SoD for the most vulnerable or mission-critical elements of the business, leaving other areas at risk.
Moreover, smaller organizations may find it particularly challenging to implement SoD as there are fewer people available to take on different parts of a task. In these cases, a single employee may be in charge of an entire process, making it challenging to separation duties effectively.
What are SoD Conflicts?
To prevent misuse of critical combinations of tasks in the process, tasks within the organization are separated. It is typically the authorization management of the company that implements preventive measures to protect against criminal activity performed by users.
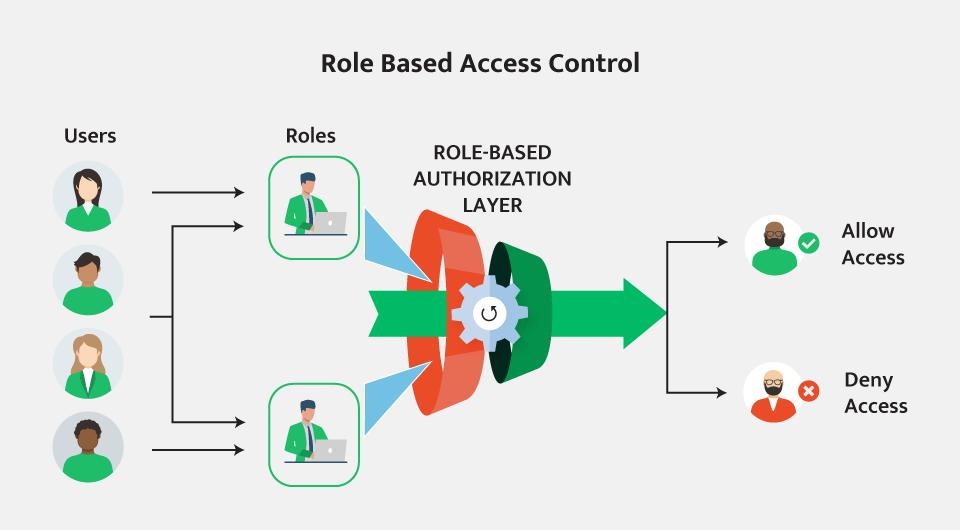
To provide these precautions against criminal activity, you must first check for SoD conflicts and perform analysis. Typically, this is done by using RBAC to analyze the roles themselves for any intrarole SoD overlaps, and then analyzing each user for inter-role SoD overlaps. SoD conflicts may occur in several areas of the company—Purchase to Pay (P2P) or Order to Cash (O2C).
When a person has the required roles needed to perform a combination of important activities in a process sequence, this is called a SoD conflict. This means that users have the potential to act in their own interest and against the interests of the company. Of course, not all conflicts mean illegal actions by users. Companies must next assess their SoD violations to ensure that SoD conflicts are not turning into risky or fraudulent behavior.
Learn more in our detailed guide to SOD conflicts
How to Reduce SoD conflicts
The first step in the SoD process is to leverage role-based access control (RBAC) to accurately provision users into systems and try to reduce potential SoD conflicts. However, SoD conflicts are an inevitable part of running a business, when evaluating the cost/benefit tradeoffs. SoD violations are like a safety net – allowing you to see when users perform a risky transaction with their combinations of policies containing an SoD conflict.
Technically, a violation occurs when the user gains control over more workflow steps than they are allowed, and uses them in parallel on one or more transactions. This could include the ability to enter vendor invoices and approve vendor payments for example. When properly applied, SoD uses internal controls to highlight these conflicts of interest and improve safety and compliance. Managing SoD through monitoring violations focuses attention and effort on actual violations of risk rather than theoretical risks raised through SoD conflicts.
What Is the SoD Matrix?
Implementing SoD can be very complex. To keep accounting roles, responsibilities, and risks clear, compliance managers use the Separation of Duties Matrix (SoD matrix). The matrix plots unique user roles once on the X axis, and the same roles on the Y axis, to identify conflicts and resolve them.
In modern organizations relying on enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, SoD matrices are generated automatically, based on user roles and tasks defined in the ERP. Each task must match a procedure in the transaction workflow, and it is then possible to group roles and tasks, ensuring that no one user has permission to perform more than one stage in the transaction workflow.
| Create requisition | Approve requisition | Create PO | Approve PO | ||||
| Process | COSO | Procedure/Function | User Group (Role) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Purchasing | Record | Create requisition | 1 | Elevated Risk | Low Risk | ||
| Purchasing | Approve | Approve requisition | 2 | Elevated Risk | |||
| Purchasing | Record | Create PO | 3 | Low Risk | Elevated Risk | ||
| Purchasing | Approve | Approve PO | 4 | Elevated Risk |
How Does Separation of Duties Impact IT Security?
SoD has two main impacts on IT security:
1. IT Security is Responsible for Implementing SoD
IT staff define the correct role hierarchy according to SoD definitions. For example, if one person has access to the software function to prepare paychecks, that same person will not have access to the software function to authorize paychecks. Similarly, IT staff need to ensure that roles do not have access to other applications or files belonging to a conflicting role.
An important part of SoD implementation is the principle of least privilege. Each user should have the minimum permissions they need to perform their duties. Even within a certain IT system, users should only have access to the data and features they specifically require.
Permissions should be regularly reviewed, and revoked in case an employee changed role, no longer participates in a certain activity, or has left the company.
2. IT Departments Need to Practice SoD Themselves
SoD within the IT department is critical—otherwise the same employee may be responsible for multiple steps of the permission assignment workflow.
Consider two examples of insufficient SoD in an IT department:
- One IT administrator is responsible for defining permissions and also assigning permissions to users. This would allow them to define super-user permission and assign it to themselves, which is not only a SoD conflict but also extremely risky.
- One user designs a security system, and is then responsible for testing and validating it. This would allow the user to design the system with vulnerabilities that would allow them to later breach it.
SoD in the IT department can prevent control failures that can result in disastrous consequences, such as data theft or sabotage of corporate systems. Different people must be responsible for different parts of critical IT processes, and there must be regular internal audits performed by users who are not part of the IT organization, and report directly to the CEO or board of directors.
Separation of Duties In Accounting
Accounting departments are traditionally the focus of SOX and similar regulations. Organizations must ensure they do not put multiple steps of a financial transaction or financial reporting flow in the hands of one person. Otherwise, there is no oversight to prevent careless or malicious users from committing acts of fraud or tampering with financial data.
A few examples of SoD conflicts in an accounting department:
- The person who prepares paychecks is not also responsible for authorizing paychecks.
- The person who deposits or withdraws cash is not the same person who reconciles bank accounts.
- The person raising purchase orders to suppliers is not the same person authorizing those purchase orders for payment.
The foundation of SoD in accounting is having several people in the accounting organization, with predefined roles that prevent SoD conflicts. In addition, there should be regular reviews by external auditors to ensure SoD is correctly maintained. Critical actions like signing high value checks or authorizing payrolls should ideally be conducted by senior executives.
How a Global Brand Achieved Full SoD Control
Scapa, a worldwide leading manufacturer of bonding products and adhesive components, needed to address SoD issues within the company – specifically in order-to-cash and procure-to-pay processes. Pathlock provided an efficient and effective SoD management tool that was running after just two days of implementation and training.
The solution quickly identified existing SoD issues and began learning the behavior of all users on all systems. After a few weeks, Pathlock’s solution delivered continuous monitoring, immediate alerts, and notifications of new SoD violations and high-risk activities throughout the organization. As a result, Scapa could quickly implement SoD on crucial processes and maintain a proactive approach to security and control.
Choosing Pathlock’s solution for our organization has proven to be an excellent decision. We have now maintained control over Separation of Duties, locating any sensitive accounts and identifying the actual user and exact time of use. These achievements were essential for protecting our SAP investment, as well as for ensuring successful audits in the future. Pathlock solicits ideas from customers to guarantee that the user’s perspective comes first. Pathlock uniquely takes users’ requests and suggestions from the field to the practical level, and on various occasions, our suggestions have been included in Pathlock’s Access Governance Solution.
Richard Symes, SAP Competence Manager, Scapa
Separation of Duties Automation with Pathlock
Pathlock’s Access Risk Analysis harnesses powerful automation to minimize risk and reduce associated costs. It streamlines identifying and remediating SoD conflicts and sensitive access risks. Traditional access control solutions only show you what users can do. Pathlock investigates transaction usage, correlates the data, and identifies what users actually did do across diverse applications, so your team can focus on the highest-priority risks first.
Our pre-built, easily customizable rulesets ensure a swift realization of value for your organization. Moreover, the automated approach simplifies compliance with regulatory standards, reducing your reliance on more traditional methods of spreadsheets, sample tests, and extensive hours of manual consolidation and review efforts.
Key Features:
Cross-Application SoD: Identifies SoD conflicts down to the permissions level for both users and roles to ensure compliant business processes, regardless of whether they are contained within a single application or across multiple applications.
Risk Dashboard: Provides a single pane of glass to monitor SoD and sensitive access risks across your on-premise and Cloud applications landscape, including risk scores and mitigation statuses.
Simulation Analysis: Forecast risk changes at the user, business role, or technical role level across applications using a flexible simulation engine. The before and after view includes usage analytics of the potential business impact.
Conflict Resolver: Expedites SoD conflict resolution by suggesting best-fit alternative roles that will maintain a user’s necessary access without containing an SoD violation.
Interested to find out more about how Pathlock is changing the future of SoD? Request a demo to explore the leading solution for enforcing compliance and reducing risk.