What is SAP Access Control?
SAP Access Control (often referred to as SAP GRC Access Control) is an enterprise-level software solution that is designed to help organizations manage user access across their IT environment, mitigate security risks, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
SAP GRC Access Control helps automate the access management process by monitoring and controlling user authorization, thereby reducing the risk of fraud and associated costs related to compliance efforts.
The latest release of SAP GRC Access Control is 12.0 SP29, which runs on SAP NetWeaver 7.52 SP01.
Read this blog, covering what is SAP GRC Access Control, its key modules, and the strategies for implementing practical access risk analysis and remediation.
Core Purpose and Functionality
SAP Access Control is an enterprise solution that enables organizations to control user access to sensitive business data and processes, preventing fraud and ensuring that users have access to the information they need according to their job role.
It automates access risk analysis, reviews, and provisioning processes to reduce the cost and time for adhering to compliance requirements such as SOX, GDPR, HIPAA, or other global compliance frameworks.
It integrates with SAP applications such as SAP Finance, SAP Sales, and SAP Distribution, as well as with non-SAP applications like Oracle and JD Edwards, allowing organizations to enforce a centralized access control policy across their entire IT system. The solution offers a unified framework for managing authorization functions.
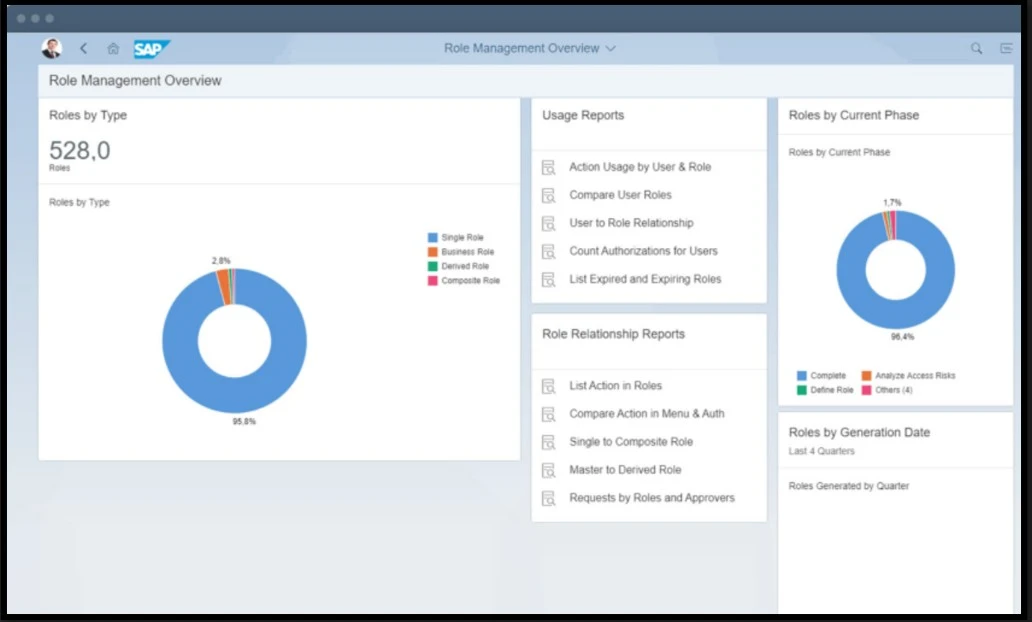
The core SAP GRC Access Control modules are:
- Access Risk Analysis (ARA)
- Access Request Management (ARM)
- Business Role Management (BRM)
- Emergency Access Management (EAM)
- User Access Review (UAR)
SAP Access Control modules enable organizations to maintain a compliant and secure environment, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and streamlining user authorization administration. It offers comprehensive dashboards and reports that provide a clear view of the organization’s risk and compliance status to management and auditors.
Key Capabilities of SAP Access Control
Analyze Risk
The core function of SAP Access Control management is to perform in-depth access risk analysis, managed by the Access Risk Analysis (ARA) module. It uses a predefined set of rules as a shared library to identify Segregation of Duties conflicts and critical access checks, based on best practices. It can be customized to meet specific business needs.
Access Control SAP provides cross-system risk analysis, which can be performed in offline mode for periodic reviews or in real-time, for example, when a new role is added to the system. It offers recommendations for removing conflicting access or reassigning roles once they are identified. Remediation controls can be documented and controlled by an approval process, as well as simulating new roles before assignment to prevent new risks from emerging.
Manage Access
The entire process of granting, changing, and revoking user access can be automated by the Access Request Management (ARM) module. Users can utilize a user-friendly self-service portal to request access, thereby reducing their dependency on the IT department. The workflow-driven approval process then routes the user access requests for approval, ensuring that access is granted after a business role owner, manager, or compliance officer reviews and approves them.
Embedded risk analysis simulates the access request process to identify SoD conflicts and flags them for approvers, providing details that offer insight to inform decisions for approval or rejection. The system automatically provisions the requested access to the targeted data or applications after approval, thereby reducing the manual process that can lead to errors.
Maintain Role
The Business Role Management (BRM) module manages the entire lifecycle of role management by providing configurable methods to define, create, and maintain business roles. Roles can be defined in business terms, aligning with actual business processes and job functions such as Accounts Payable Clerk or Sales Order Processor, making them easier to understand and manage. This module also provides tools for role analysis and optimization, eliminating redundancy and unnecessary access, which ensures that roles adhere to the principle of least privilege.
Certify Authorizations
The SAP Access Control’s User Access Review (UAR) module ensures that periodic reviews are automated and provide certifications of authorizations, a key requirement for compliance and audit. Additionally, workflows are adequately triggered to send review requests to role owners or managers. Reviewers who can certify that role assignments and user access are still necessary can use this process to identify and remove redundant access that has accumulated over time. This module also manages the automation of mitigating controls review to ensure that they are still working as intended.
Monitor Privileges
The Emergency Access Management (EAM) module, also known as “Firefighter,” provides a secure and documented method for managing temporary elevated access during emergencies. It enables designated users to gain temporary administrative access for resolving critical issues within a controlled environment. All activities during this session are thoroughly logged, including details of transactions executed by the designated user. Logs can be sent to specific individuals for review and approval to ensure accountability, along with configured notifications for sensitive actions performed, enabling them to take immediate action. SAP Access Control provides customizable dashboards and reports, offering a detailed view of emergency access usage and risk analysis for monitoring and auditing purposes.
SAP GRC Access Control Integration
SAP GRC Access Control can integrate with a wide range of systems to provide access governance, risk analysis, and automatic access provisioning across an enterprise’s IT landscape, including both SAP and non-SAP, on-premises and cloud-based applications, as well as identity management platforms.
SAP Applications
SAP Access Control can integrate natively with the following SAP solutions for centralized risk management and user access provisioning, providing a single source of truth for access governance.
- SAP S/4HANA On-Premise: Integrating with S/4HANA is the core functionality of SAP GRC, enabling organizations to analyze and manage SoD risk analysis and user access risks, including Fiori apps, within the S/4HANA system.
- SAP SuccessFactors: SAP GRC can directly connect with SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central for access risk analysis and automated user access provisioning based on the employee lifecycle events, such as hiring, role changes, or termination processes.
- SAP HANA DB: The GRC solution can integrate directly with the SAP HANA database to analyze and manage permissions and roles on the database level, which is crucial for protecting the data layer. EAM module features are also extended to the HANA database.
- SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central Payroll: Similar to Employee Central’s broader integration, SAP GRC can integrate with the payroll module for specific payroll-related functions’ risk analysis.
- SAP Process Control: SAP GRC Access Control and SAP Process Control are tightly integrated and share the same organizational structure. Controls created in Process Control can be used in Access Control to identify SoD risks.
- SAP Cloud Identity Access Governance: SAP Cloud IAG can function as a bridge between on-premises GRC Access Control features and cloud applications, allowing them to use their existing GRC solution to manage access in the cloud.
Non-SAP Applications
SAP GRC Access Control offers extended integration beyond the SAP ecosystem by including other non-SAP enterprise applications, such as Oracle, JD Edwar, or PeopleSoft. This integration enables organizations to conduct cross-platform SoD risk analysis and user access provisioning from a centralized platform. This integration can be achieved using standard or custom connectors.
Identity Management
SAP GRC Access Control integrates with identity management systems, both SAP Identity Management and non-SAP Identity Management applications, via web services. It combines identity lifecycle management with access governance. IDM manages automated user provisioning, and GRC ensures risk-free and compliant user access provisioning by conducting checks before assigning permissions. Integration with non-SAP applications via web services enables organizations to utilize GRC’s risk analysis and approval workflows within their own IDM processes.
Cloud Applications
As organizations proactively adopt cloud solutions and migrate their existing applications to the cloud, access governance becomes increasingly critical. SAP GRC offers integration with its cloud solutions, including SAP Ariba, SAP Concur, and SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central. SAP SuccessFactors is supported for direct integration, while SAP Ariba and SAP Concur can be integrated using SAP Cloud Identity Access Governance or SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) cloud connectors. This hybrid approach enables the on-premises access control system to synchronize user and role data between the GRC system and cloud applications.
Custom / Non-Standard Integration
Pathlock is a leading IGA and GRC solution provider that offers a suite of connectors for applications lacking standard integration connectors, enabling seamless connections between its solutions and third-party identity, access, and security solutions. Organizations can quickly and easily build no-code connectors and integrate their applications and systems with Pathlock Cloud. Pathlock goes beyond typical user entitlement data, extracting fine-grained permissions from multiple applications. This enables organizations to perform risk analysis at the permission level, rather than role-based assignments. The connectors offer the following key features.
- Analysis of SoD and sensitive users and roles access.
- Creation, modification, locking, and unlocking users.
- Users and Roles addition and removal.
- User Activities logging.
- Elevated access sessions for audit readiness.
Navigation Interfaces
Login Methods
SAP Access Control provides several navigation interfaces tailored to the unique needs of users, serving as primary gateways for user interaction with various application functions. There are three primary interfaces for users to log in and access the features of SAP Access Control.
- SAP Fiori Launchpad (FLP)
- SAP NetWeaver Business Client (NWBC)
- SAP Enterprise Portal (Portal)
SAP Fiori Launchpad (FLP) Navigation
Fiori Launchpad is a recommended and mainly used interface. It is a modern, web-based, and role-based entry point UX for users, offering a personalized and responsive interface on various devices, including desktops, mobiles, and tablets.
Home Page
The Fiori Launchpad home screen displays several tiles as a graphical entry point, representing specific applications or functions. These tiles are displayed based on the user’s role. Users see only tiles related to their job functions.
The home page of a user is highly customizable. Users can add, remove, rename, and reorder them according to their personalization requirements.
These tiles can provide real-time information or live status indicators, such as the number of pending requests, which helps users prioritize their work.
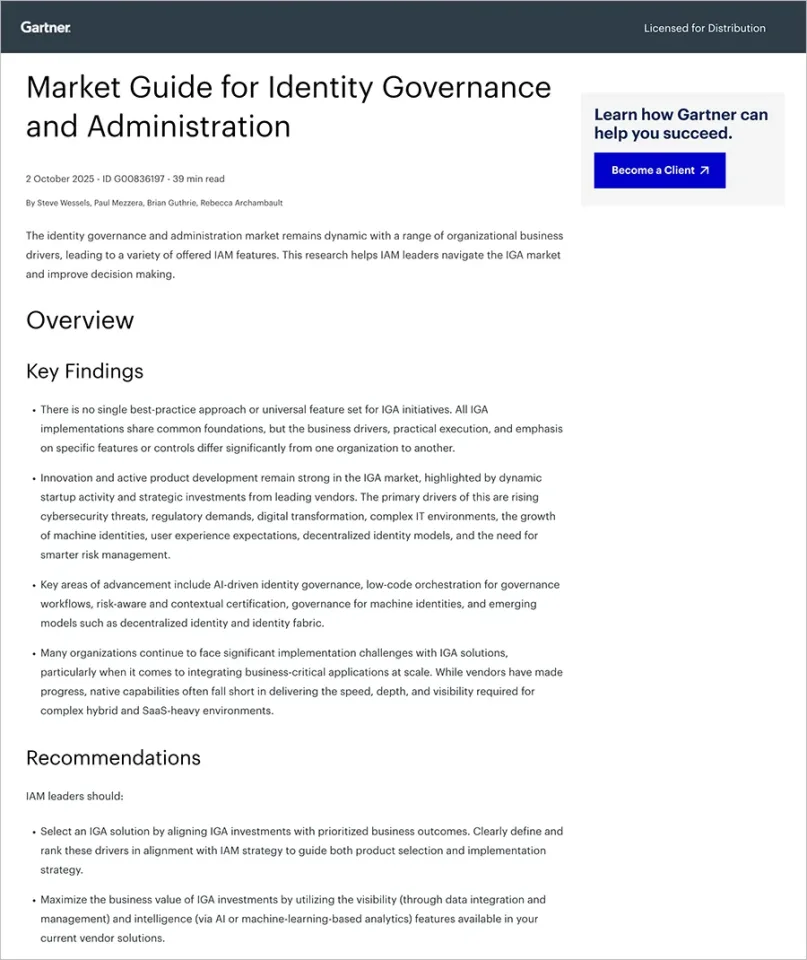
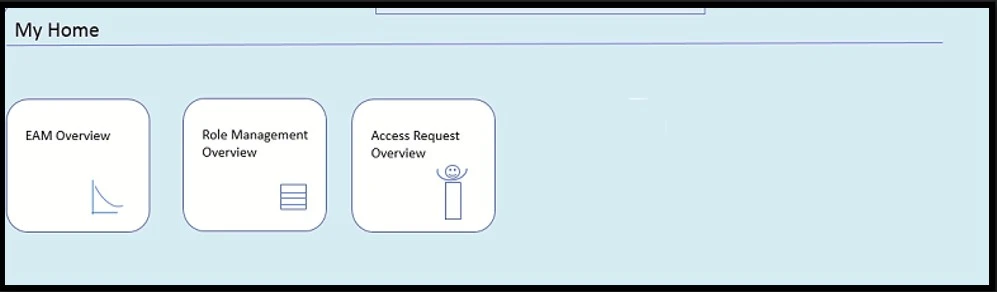
SAP Fiori provides a catalog of tiles. Users can add any tile for which they are authorized to their home page. For example, users can add one of the key SAP GRC Access Control overview tiles, such as Access Request Overview, Role Management Overview, or Emergency Access Management Overview. Below is a sample home page illustration.
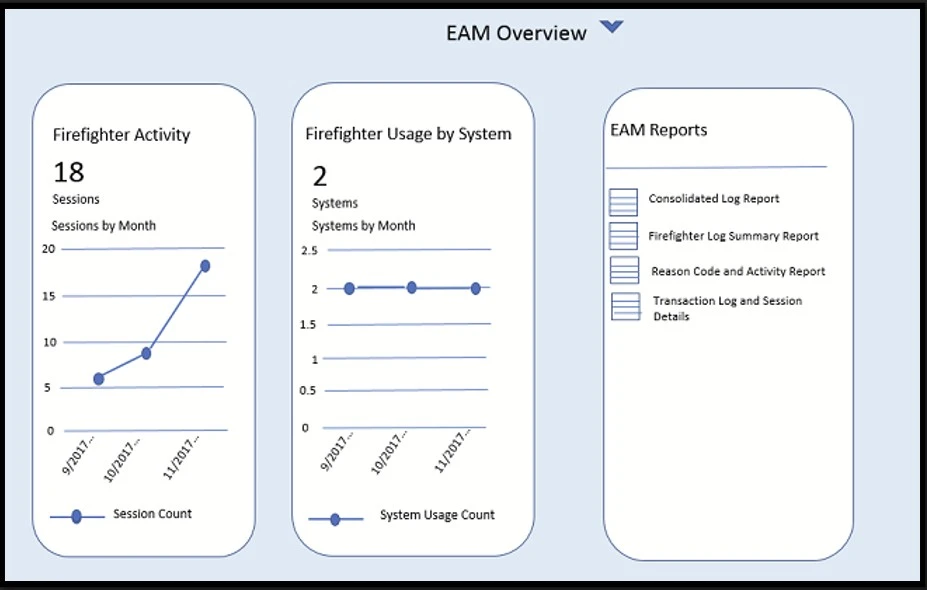
SAP Fiori offers various types of overview page tiles, including Analytical Tiles, to provide up-to-date visual information, such as a Firefighter Activity graph or chart. A detailed report can be linked and presented when users click on these tiles. Other types of tiles include List Tiles, which are simple in form, directly connected to a related report, such as a list of EAM reports. In contrast, Analytical tiles display charts and graphs in a visual format, linking a report to a tile. Below is an example illustration of the EAM overview tile, showing a mockup of analytical and list tiles.
SAP NetWeaver Business Client (NWBC) Navigation
A desktop-based client that integrates legacy SAP GUI-based transactions into modern Web Dynpro applications. This interface is suitable for administrators and power users who require access to both classic and contemporary transactions.
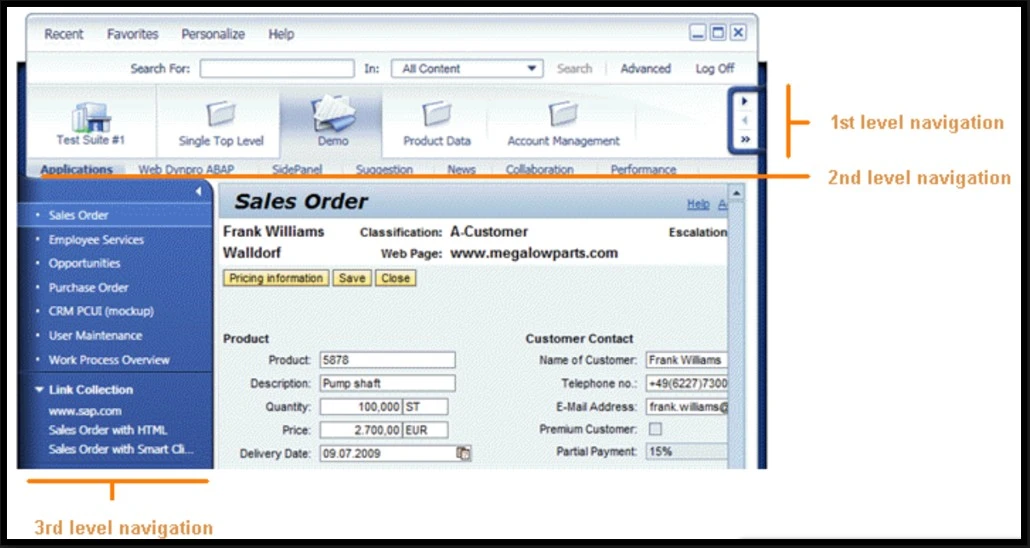
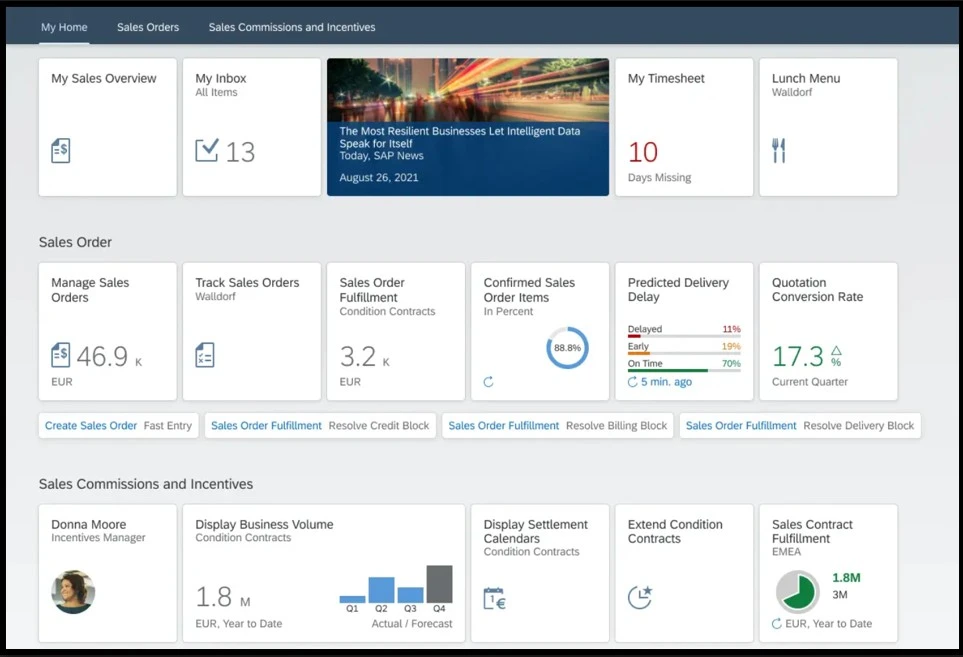
Navigation in SAP Business Client is grouped into Work Centers, which are displayed at the top of the main screen. These work centers are further grouped into related activities, tasks, and functions. Main Work Centers for SAP Access Control are as follows:
- My Home: A customizable dashboard where users can access their personal tasks, such as user profile settings or the work inbox for approving access requests.
- Setup: GRC environment configurations can be managed in this work center, such as access control setup and administration, defining owners and systems, or master data management.
- Access Management: All the core functions of user access management, such as Access Risk Analysis, Business Role Management, Access Request Management, and role management, are available in this work center.
- Reports and Analytics: All the standard and custom reports and compliance dashboards, including SoD analysis, are accessible in this work center.
These are the standard set of work centers offered by SAP Business Client, but administrators can customize them according to their organizational structure.
SAP Enterprise Portal
A web-based portal that serves as a single point of access for different company applications, information, and services, providing a merged view for customers, suppliers, employees, and partners. Various SAP and non-SAP applications can be integrated in the SAP Enterprise portal to offer a role-based view of information and business processes.
Core Functional Modules
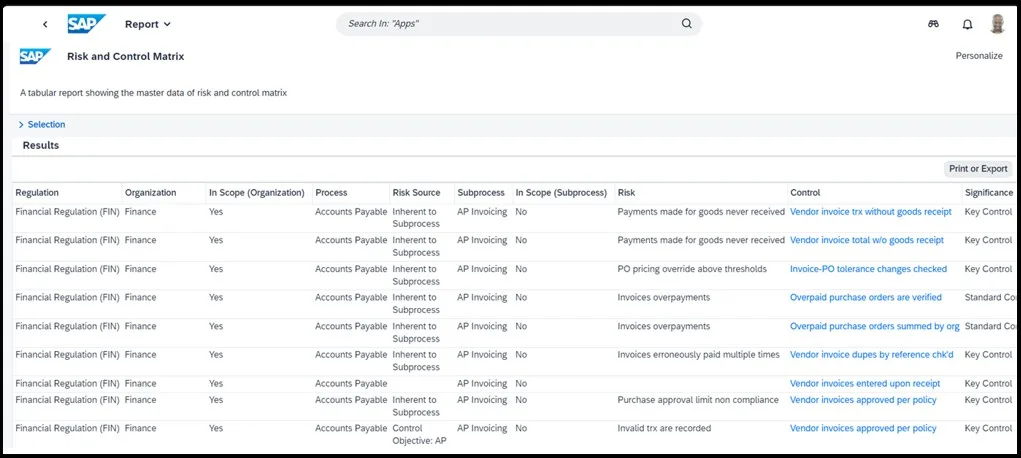
Risk Analysis and Remediation
The Access Risk Analysis (ARA) module is the backbone of SAP GRC Access Control, enabling the identification, analysis, and resolution of critical access risks through the following capabilities.
Risk Identification and Policy Enforcement
ARA defines and enforces access control policies across all SAP and non-SAP systems to find and evaluate potential access risks and violations, such as SoD, ensuring compliance.
Predefined Rule Sets
The module provides risk catalogs and predefined rule sets for standard solutions, such as SAP ERP, CRM, and S/4HANA, as well as for non-SAP systems, including Oracle, JD Edwards, and PeopleSoft. Organizations can customize these rule sets according to their specific requirements and business processes, such as Finance, HR, or Sales.
Risk and Rule Set structure
Risks are categorized by business processes and classified as either a critical action, e.g., high-risk transactions with privileged accounts, a critical permission, e.g., risk at object-level authorization, or SoD risk, such as conflicting activities performed by a single individual. Rule sets are similarly organized by business process, forming the building blocks for the risks, and can be classified for a single system or across systems.
Analysis Modes and Simulation
Risk analysis can be performed at several levels, including a specific user, a specific role, a group of users, a business process, or an access risk ID for reporting purposes. Analysis can be conducted in several modes, including real-time during a request, on demand, on an ad hoc basis, or offline batch risk analysis for the entire application. ARA also provides a risk simulation feature, known as a “What-if” scenario, which allows administrators to simulate the impact of user access provisioning or role design, thereby preventing new conflicts from arising because of changes or access provisioning.
Remediation and Mitigation
Upon identifying risks, administrators can remediate them by removing or adjusting conflicting access. If the risk is critical to the business, a mitigating control can be selected from the control catalog and applied to a user to manage the risk.
Dashboards and Reports
Graphical dashboards and detailed reports are provided to display an organization’s risk posture and remediation actions. These dashboards are powered by background jobs to update them with the latest data.
Risk Analysis Dashboard
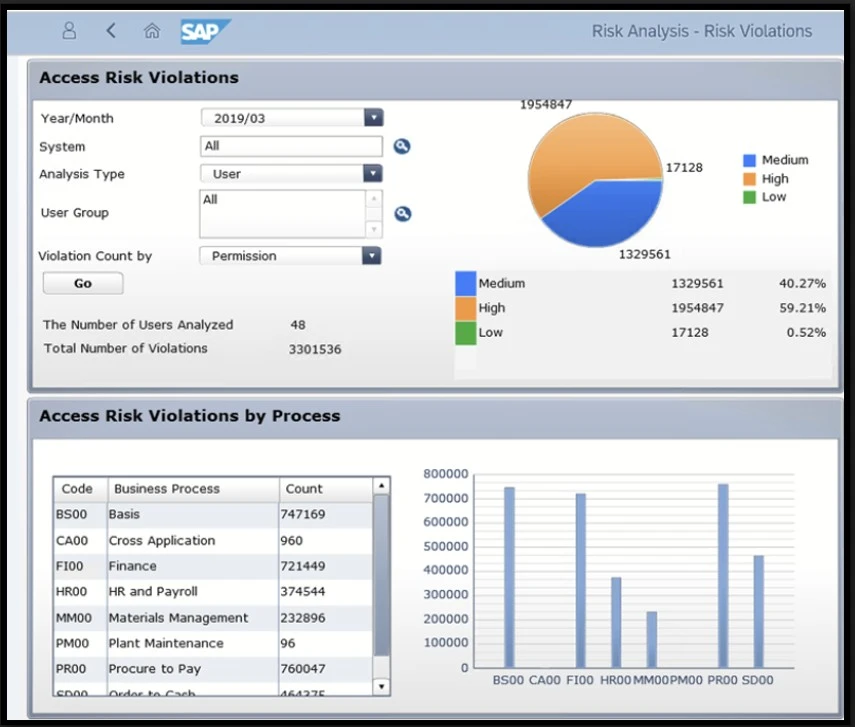
Ad Hoc Risk Analysis
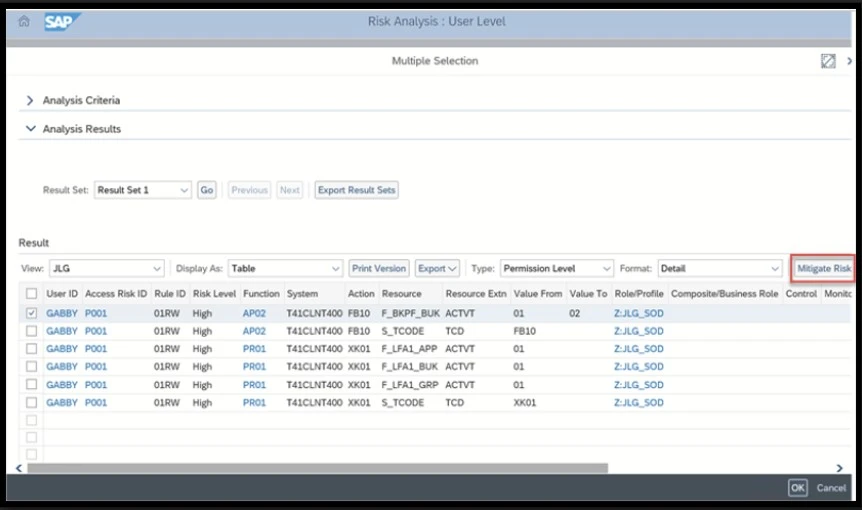
Access Request Management
ARM module provides automation of the entire access lifecycle, from user request to approval and then access provisioning, ensuring compliance and audit readiness.
Compliant Provisioning
ARM offers compliant user provisioning and deprovisioning based on a workflow-driven method and real-time risk analysis during the request process, which prevents new risks and violations before granting access.
Self-Service and Automation
ARM offers a user-friendly self service portal for users to request access for themselves or for others. This process initiates the workflow automatically, routing the request to the appointed approvers or managers and then provisioning access in SAP or non-SAP applications.
Flexible Workflow
The ARM module utilizes a flexible, multistage, multipath (MSMP) workflow engine, enabling organizations to design highly customizable workflows that meet their specific business requirements. These workflows can include approval paths for request access, as well as support for Risk Maintenance, Role Maintenance, Function Maintenance, Mitigation Maintenance, and User and Compliance Certification.
Auto Provisioning
ARM automatically creates the user master record in identity management systems and provisions requested access upon final approval, eliminating the need for manual intervention by security teams. This allows them to focus on security incidents rather than manually creating users and assigning permissions and roles.
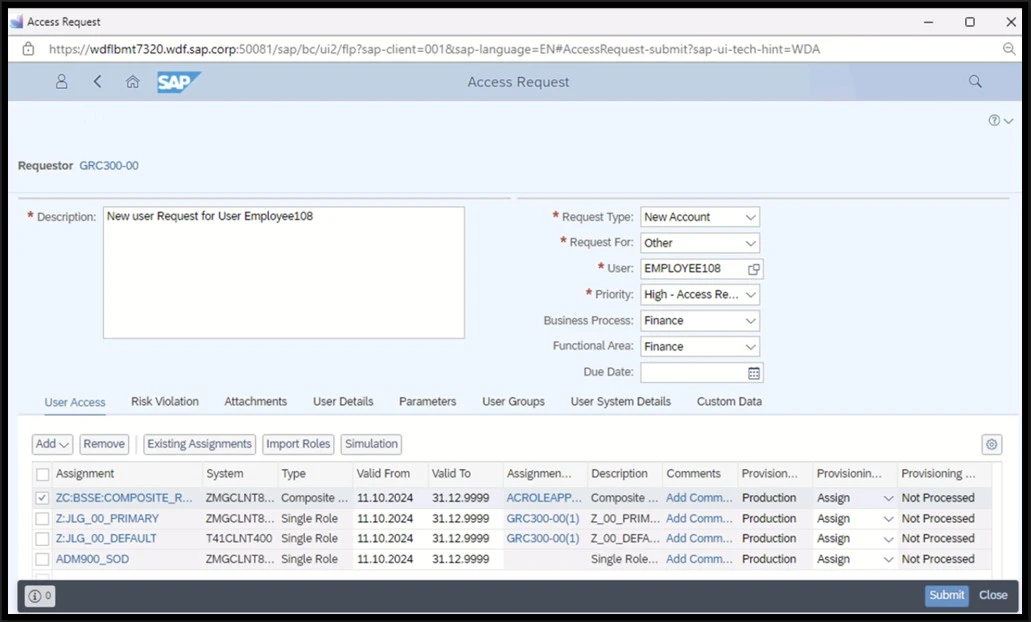
Business Role Management
Centralized Role Management
The BRM module provides a structured and centralized environment for managing the complete business role lifecycle, from defining a role to maintaining it and ensuring compliance with regulations, serving as a framework for audit purposes.
Best Practice Methodology
BRM employs a customizable best practices methodology that guides distinct phases of business role management. These include defining roles, maintaining authorizations, assessing access risks, configuring request approval, generating roles, and managing test cases and results.
Compliance and Audit Trail
BRM tracks all changes, such as workflow approvals and risk analysis, performed in relation to a role, providing a complete audit trail throughout the entire business role management process.
Periodic Reviews
The Business Role Management module supports periodic review processes, such as Role Reaffirmation, where the business need for a role must be reconfirmed by the role owner, and Role Certification, where the role’s content must be certified before it becomes active. This ensures that the role is relevant and compliant.
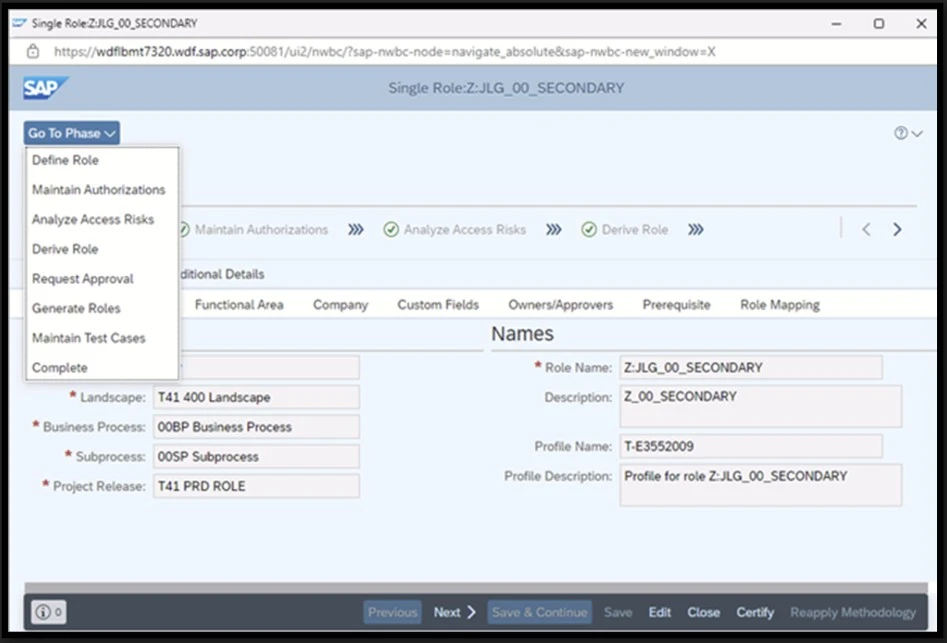
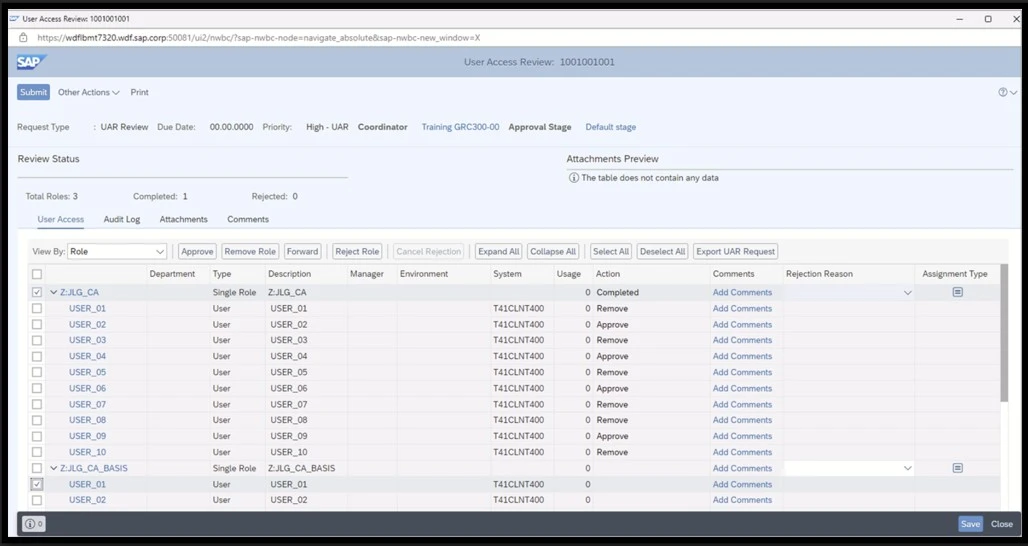
Access Certification and Review
The User Access Review (UAR) module in SAP GRC Access Control enables business owners to review and approve user access rights, certifying that the user’s access is still valid and necessary. UAR offers the following functions to support access certification, audit, and compliance.
User Access Review
A workflow-driven process that utilizes a multistage and multipath (MSMP) approval process, allowing managers or role owners to review their assigned access quickly. This process triggers de-provisioning upon flagging for removal and certifies upon approval.
SOD Review
Like UAR, a workflow-driven process enables managers or risk owners to review and certify the segregation of duties conflicts and critical action risks. Managers then decide whether the conflicting access is appropriate; if not, contradictory access is removed. Both approval and removal decisions are automated and documented.
Role Reaffirmation
This process is similar to user access review but is not workflow-driven. A notification is sent to the role owner for role reaffirmation when the defined date approaches. The role owner then decides whether the role is still valid for business purposes or proposes its removal.
Role Certification
Role certification is also notification-based and is defined at the time of role definition, with a specific date, to determine later if the role is still correctly designed, including proper access and permissions. When the date approaches, a notification is triggered to the role content approver to certify the content of the role.
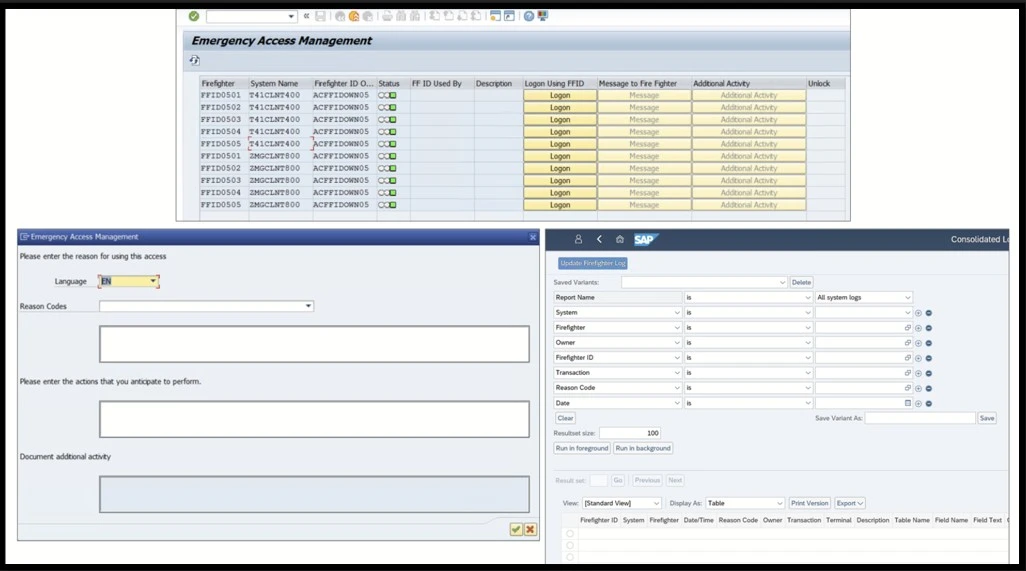
Emergency Access Management (EAM)
The EAM module, often referred to as Firefighter, provides a secure and audited process for defining, managing, monitoring, and temporarily granting privileged access to tackle emergencies.
- This process enables designated users with Firefighter IDs with elevated permissions, which are controlled and approved by a Firefighter process owner and monitored by a Firefighter controller.
- Firefighter owner approves an access request to a Firefighter ID using workflow; the user then checks out the ID to open a session to the target system or application.
- EAM creates a detailed log of performed actions during this session and sends it to the Firefighter controller for review.
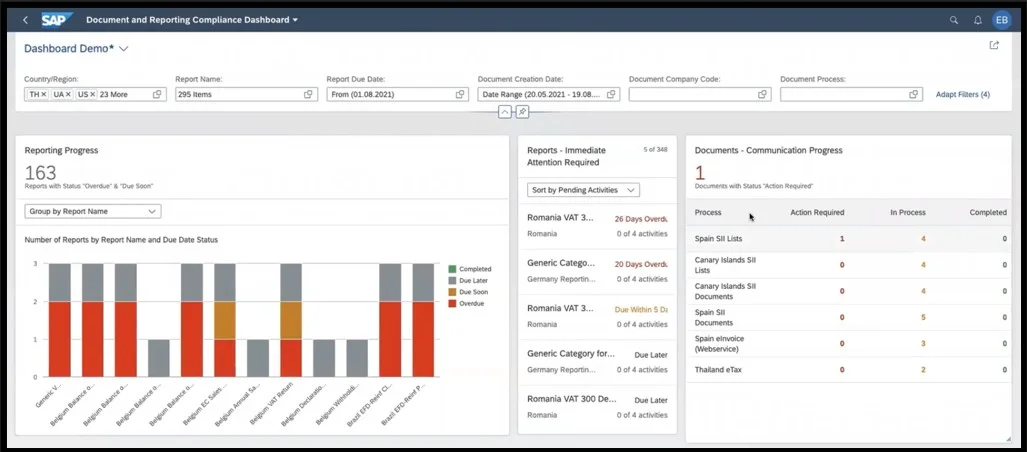
Monitoring and Reporting (Audit and Compliance Reporting)
SAP GRC Access Control offers pre-configured, customizable, and standard dashboards, monitoring, and reporting functions to meet management, compliance, and audit requirements, providing insight into who requested, approved, and provisioned access.
- Provide reports for transaction usage, risk mitigation, and emergency access grant.
- These reports include access rules, mitigation control, user risk violation, role risk violation, action usage, role usage, and change log.
- The monitoring and Alert function gathers data on user access or when a required mitigating control is not performed and generates alerts for critical access or conflicting SoD access to managers or risk owners.
- Dashboards provide a visual representation of the overall risk posture of an organization, including risk exposure, mitigating controls, and alerts, in a user-friendly graphical view to upper management and risk owners.
Compliance Phases and Governance Strategy
Primary Purpose: Adhere to compliance requirements
The primary purpose of SAP GRC Access Control is to ensure that companies adhere to compliance requirements and reduce their security and audit risks by offering a structured approach to manage and maintain access governance. This approach enables companies to meet regulatory compliance frameworks, such as SOX, GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO 27001, and enforce internal policies.
SAP GRC Access Control enables enterprises to combine automation, monitoring, and recertification to minimize audit findings, reduce the operational cost of compliance, prevent fraud and errors, and continuously prove compliance to auditors and regulators.
Three Phases of Implementation
SAP GRC Access Control is designed to be divided into three phases for a compliance strategy, including Get Clean, Stay Clean, and Stay in Control.
Get Clean
In this phase, organizations can focus on understanding and identifying existing access risks in their environment using the risk analysis and management capabilities of SAP Access Control, such as SoD and critical risk identification. Once the risks are identified, the IT team should work to remediate and mitigate the risks to clean the environment, such as removing unnecessary or conflicting access from roles and users. If the risks cannot be eliminated, then they should define the mitigating controls, document them, and assign these controls to the corresponding risks. Business teams should adjust their processes to reduce potential risks by collaborating closely with the IT team.
Stay Clean
The “Stay Clean” phase focuses on maintaining a clean system after the initial cleanup is complete. Organizations can implement daily SAP risk analysis and compliance checks in access management tasks to prevent new risks from emerging in the system. This can be achieved using the Business Role Management module, the Access Request Management module for user provisioning, and the Emergency Access Management module for privilege management.
Stay in Control
This is a continuous phase to ensure that organizations maintain a clean system over time by using monitoring, periodic reviews, and regular compliance certifications. Periodic user access reviews can be conducted and automated for the recertification of assigned access, SoD reviews, and Firefighter ID reviews by managers, role owners, or risk owners. This entire process of periodic reviews and recertification demonstrates that an organization’s access control framework is effective and compliant over a long period of time.
Technical Architecture and Supported Systems
SAP Access Control architecture is designed to provide wide compatibility and extensibility as a central access governance platform. This can be achieved using a combination of plug-ins for SAP systems and several connectors for non-SAP, cloud, and identity management applications.
- SAP Access Control serves as an add-on to SAP NetWeaver, integrates with all SAP NetWeaver-based systems such as SAP ERP, SAP S/4HANA, SAP CRM, SAP SRM, SAP SCM, and SAP BW/BI.
- A specific plug-in GRCPINW, which is native to NetWeaver, is required to be installed on all connected systems.
- SAP Access Control 12.0 supports plug-in version v1100 and v1200 but not the older version v1000.
- Organizations can use the GRCPIERP plug-in to use HR related triggers, such as for new hire, employee transfer, or termination, for automating the access requests.
- Remote Function Call (RFC) connectors can be used to pull user and role data for analysis from target systems once the required plug-ins are installed.
- As mentioned earlier, Pathlock adapters can be used to extend the reach of SAP Access Control to the applications that lack the standard or out-of-the-box connectors.
Technical and Security Resources
SAP provides several resources to support customers in implementing, securing, and maintaining their SAP Access Control environment.
SAP Help Portal
SAP Help Portal is a central documentation repository for all SAP products. It provides in-depth guidance for the installation and configuration of each module of GRC SAP Access Control, including step-by-step instructions and best practices for deploying various components, as well as technical articles tailored to configuration and optimization that address business needs.
SAP Help Portal for SAP GRC Access Control
Data Security
SAP implemented technical and organizational measures, including data encryption in transit and at rest, role-based access control (RBAC), regular security updates, and continuous monitoring, to protect its customers’ data.
Explore more about SAP’s data integrity, availability, and confidentiality: Data Security
Trust Center
SAP has built trust with its customers over the period by providing transparency, accountability and secure cloud operations, such as offering easy access to security measures documentation, data privacy policies and status of cloud services operation, below is the link to their Trust Center page for more learning, it provides updates on Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), NIS2 Updates and a “My Trust Center” area for SAP customers and partners with additional documentation.
Compliance
SAP adheres to a wide range of international compliance standards to support customers’ compliance needs and provide the necessary documentation to facilitate audits. SAP offers compliance certifications, attestations, and reports for ISO 27001, ISO 9001, SOC 1, and SOC 2, among other standards.
SAP regularly monitors worldwide regulatory standards, such as GDPR, DORA, and NIS2, and provides necessary documentation on their updates.
Learn more about SAP compliance by following the link: SAP Compliance Offerings – Certificates, Reports, and Attestations.
Conclusion and Value Proposition
Overall Summary
SAP GRC Access Controls offers confident access control and compliance management through its five core modules: Access Risk Analysis, Access Request Management, Business Role Management, Access Certification, and Emergency Access Management.
Organizations can confidently manage and control their user access, enforce compliance, and mitigate security risks across their entire IT environment. Its power comes from an integrated risk analysis engine connected to role management and workflow-driven user access provisioning.
SAP Access Control provides advanced analytics and standard reporting features, including ad-hoc reports, batch analysis reports, analytical dashboards, and proactive alerting.
Benefits
SAP Access Control offers numerous key benefits. Some notable value drivers are:
- The solution provides centralized access governance to define, enforce, and monitor access policies across SAP and non-SAP applications.
- The solution offers end-to-end user lifecycle control with automation and security, from hiring to role changes, certification, and termination to access revocation.
- The solution provides real-time compliance enforcement by embedding risk analysis into access requests, role management, and role maintenance, which also provides proactive monitoring instead of reactive remediation.
- The solution provides integrated risk and privilege monitoring with comprehensive dashboards, reports, and alerts, including temporary privileged access. It doesn’t just identify and analyze risks but also monitors how risks are being managed.
- The solution is scalable across SAP and non-SAP environments through a wide range of plug-ins, connectors, and adapters.